Educational Developments in Punjab Literacy Rate 2025 Statistics
Punjab literacy rate 2025 stands at 77.5%, reflecting a steady improvement from previous years. This progress underscores the state’s commitment to enhancing educational outcomes for its residents. However, challenges persist, particularly concerning gender disparities and the rural-urban divide in literacy levels.
Current Literacy Statistics in Punjab 2025
The 2025 literacy data for Punjab reveals:
- Overall Literacy Rate: 77.5%
- Male Literacy Rate: 82.1%
- Female Literacy Rate: 72.8%
- Rural Literacy Rate: Approximately 73%
- Urban Literacy Rate: Approximately 83%
These figures indicate a positive trend in educational attainment. Nonetheless, the noticeable gap between male and female literacy rates, as well as between rural and urban areas, highlights areas requiring focused attention.
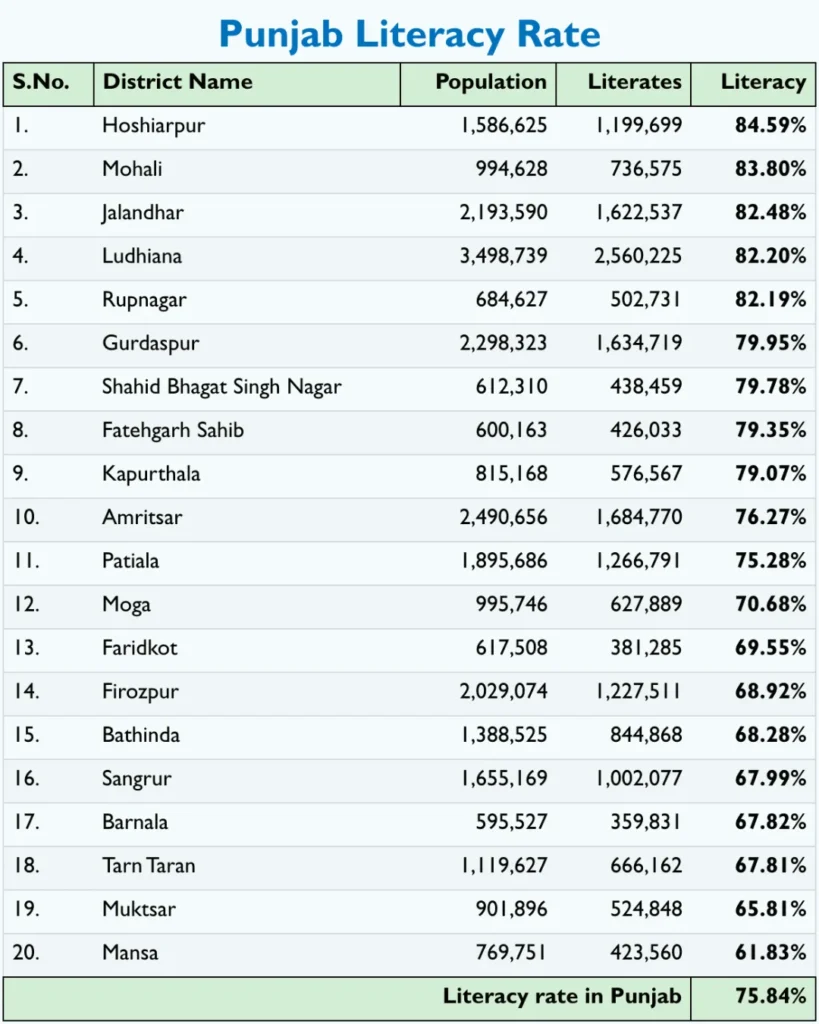
District-wise Literacy Rates
An analysis of literacy rates across Punjab’s districts shows significant variations:
- Highest Literacy Rates:
- Hoshiarpur: 84.59%
- Mohali: 83.80%
- Jalandhar: 82.48%
- Ludhiana: 82.20%
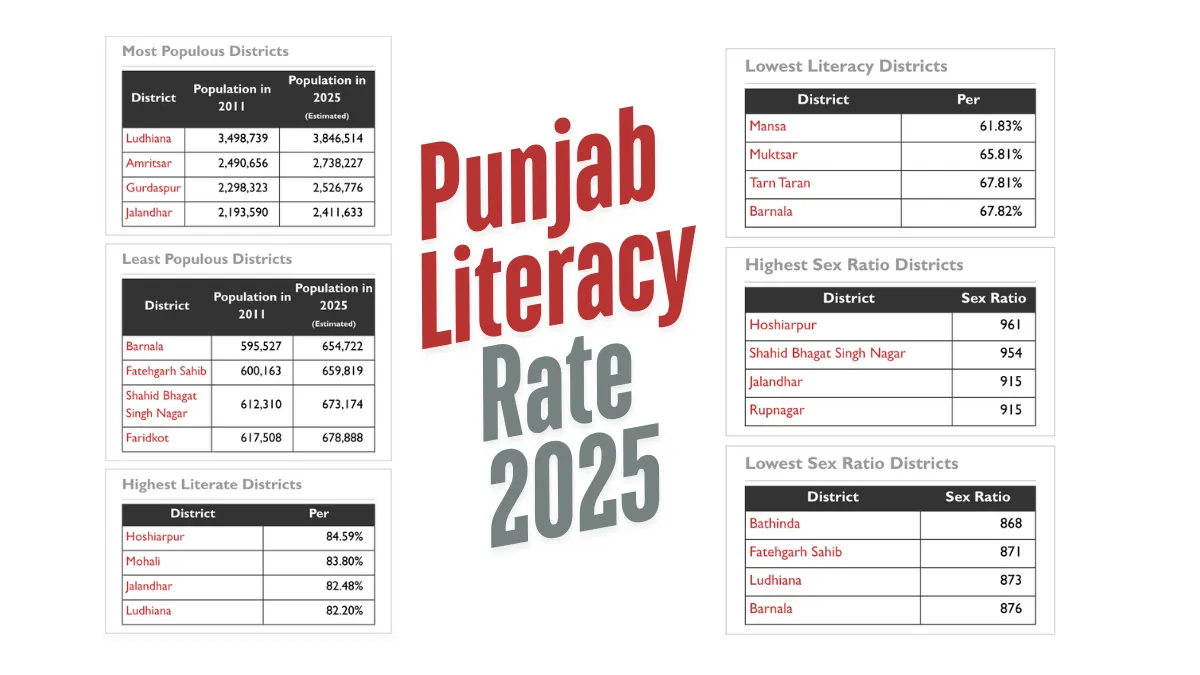
- Lowest Literacy Rates:
- Mansa: 61.83%
- Muktsar: 65.81%
- Tarn Taran: 67.81%
- Barnala: 67.82%
These disparities suggest that while certain districts have made commendable progress, others lag behind, necessitating targeted interventions to uplift educational standards uniformly across the state.
Government Initiatives and Punjab Educational Programs
To address these challenges, the Punjab government has implemented several initiatives:
- Free and Compulsory Education Act: Ensures free education for children up to 14 years, leading to increased primary school enrollments.
- Adult Literacy Programs: Focus on educating adults, especially women in rural regions, to boost overall literacy.
- Digital Learning Initiatives: Introduction of digital resources and smart classrooms in government schools to modernize education.
- Scholarship Schemes: Financial support for economically disadvantaged students encourages higher education pursuits.
- Teacher Training Programs: Ongoing professional development ensures educators are equipped with effective teaching methodologies.
These programs aim to create an inclusive educational environment, promoting equal opportunities for all segments of the population.
Challenges in Achieving Higher Literacy Rates
Despite these efforts, several obstacles hinder the attainment of higher literacy rates:
- Gender Disparity: Cultural and economic factors, particularly in rural areas, limit educational opportunities for girls, contributing to the existing literacy gap.
- Rural-Urban Divide: Rural regions often face inadequate educational infrastructure and resources compared to urban centers.
- School Dropout Rates: High dropout rates, especially at the secondary level, adversely affect overall literacy statistics.
- Quality of Education: While enrollment numbers are rising, ensuring the quality of education remains a pressing concern.
Addressing these issues requires comprehensive strategies that encompass societal, economic, and infrastructural reforms.
Also Read: NH Punjab – Lifeline Connecting Culture and Commerce
Impact of Literacy on Punjab Economy and Society
Enhanced literacy rates have profound implications for Punjab’s socio-economic landscape:
- Economic Growth: An educated workforce attracts better employment opportunities, fostering economic development and reducing poverty levels.
- Social Empowerment: Education empowers individuals, leading to improved healthcare, reduced child marriage rates, and greater social mobility.
- Informed Citizenship: Literate citizens are better equipped to participate in democratic processes and advocate for their rights.
Thus, promoting literacy is pivotal not only for individual advancement but also for the state’s holistic development.
Also Read: Literacy Rate in Punjab 2024: Stats, Initiatives, Future
Future Prospects and Proposed Measures
Looking ahead, Punjab aims to elevate its literacy rate beyond 85% by 2030. Proposed measures to achieve this goal include:
- Expanding Adult Education Programs: Incorporating vocational training and skill development to make adult education more comprehensive.
- Bridging the Digital Divide: Ensuring rural students have access to digital tools and internet connectivity to facilitate modern learning.
- Focusing on Female Education: Implementing initiatives that encourage girl child education and dismantle socio-cultural barriers.
- Improving School Infrastructure: Investing in facilities like smart classrooms, libraries, and sports amenities to enhance the learning environment.
- Robust Monitoring Systems: Establishing mechanisms to assess school performance, teaching quality, and student outcomes to maintain educational standards.
By adopting these strategies, Punjab is poised to make significant strides in its educational landscape, ensuring that literacy serves as a cornerstone for the state’s future growth and prosperity.

